Learning Spanish 101
- Introduction to Spanish
- Everyday Vocabulary
- Conversational Spanish
- Intermediate Grammar
- Travel Vocabulary
- Business Spanish
- Spanish Culture
- Advanced Grammar
- Spanish Literature
- Spanish in the Media
- Review and Practice
Spanish Culture
An Overview of Spanish History
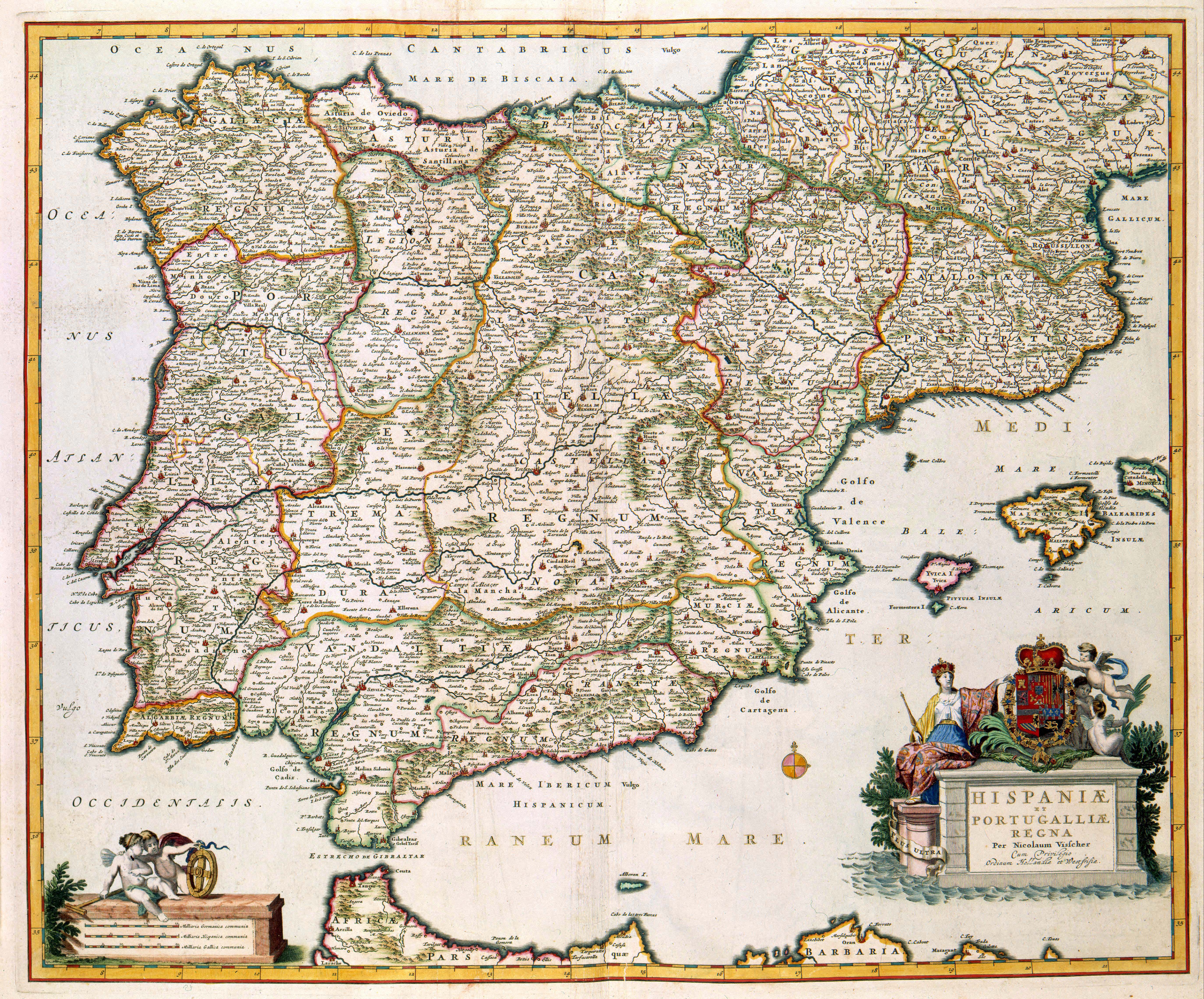
Aspect of history.
Spanish history is a rich tapestry of cultures, conquests, and revolutions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the key periods and events that have shaped Spain as we know it today.
The Iberian Peninsula: Prehistoric Cultures and Roman Rule
The Iberian Peninsula, home to modern-day Spain and Portugal, has been inhabited for hundreds of thousands of years. Prehistoric cultures left behind fascinating artifacts, including the famous cave paintings at Altamira. The region was later dominated by the Celts and Iberians before falling under Roman rule in 206 BC. The Romans left a significant cultural imprint, including the Latin language, from which Spanish evolved.
The Visigothic Kingdom and the Islamic Conquest
After the fall of the Roman Empire, the Visigoths, a Germanic tribe, established a kingdom in Spain. However, their rule was short-lived. In 711 AD, Muslim armies from North Africa invaded the peninsula, marking the beginning of the Islamic Conquest. The period of Muslim rule, known as Al-Andalus, saw a flourishing of science, art, and culture.
The Reconquista and the Rise of Christian Kingdoms
The Reconquista, a period of nearly 800 years, was marked by Christian kingdoms in the north gradually retaking territory from Muslim rule. This culminated in 1492 with the fall of Granada, the last Muslim stronghold. The same year, Christopher Columbus, sponsored by the Catholic Monarchs Ferdinand and Isabella, discovered the New World.
The Spanish Empire: Exploration and Colonization
The discovery of the Americas marked the beginning of the Spanish Empire, one of the most powerful in history. Spain's global exploration and colonization brought immense wealth and expanded the Spanish language and culture worldwide. However, it also led to the exploitation and decline of indigenous populations.
The Spanish Civil War and Franco's Dictatorship
The 20th century was a turbulent time for Spain. The Spanish Civil War (1936-1939) was a devastating conflict between the Republicans, who supported a liberal democracy, and the Nationalists, led by General Francisco Franco. Franco's victory established a dictatorship that lasted until his death in 1975.
Modern Spain: Transition to Democracy and the European Union
After Franco's death, Spain transitioned to a constitutional monarchy under King Juan Carlos I. The Spanish Constitution of 1978 established Spain as a parliamentary democracy. In 1986, Spain joined the European Union, marking its integration into the European community.
Spanish history is a fascinating journey through time, marked by diverse cultures, powerful empires, and transformative events. Understanding this history provides invaluable context for the Spanish language and culture.